Wall Street Eyes Inflation Trends as 2025 Approaches
As 2025 approaches, Wall Street watches inflation, trade policies, and Federal Reserve actions closely to gauge economic challenges and growth prospects.

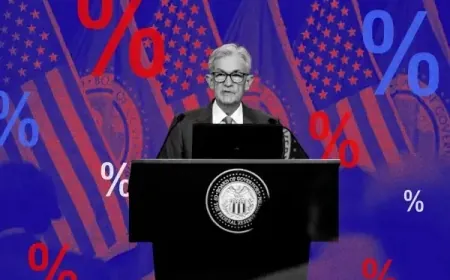
As 2025 draws near, Wall Street remains deeply focused on inflation, a persistent concern that has shown signs of easing but still remains above acceptable levels. Financial analysts and policymakers are preparing for a year marked by ongoing price pressures and potential shifts in monetary policy that could significantly impact the economy.
Inflation Stays Stubbornly High Despite Gradual Improvements
While inflation showed some signs of slowing in 2024, it remains well above the Federal Reserve’s 2% target. “Although we are seeing gradual improvements, inflation is still too high for the Fed’s comfort,” said Matthew Luzzetti, chief economist at Deutsche Bank. As of November, key indicators such as the core Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) index and the core Consumer Price Index (CPI) showed annual increases of 2.8% and 3.3%, respectively.
The primary drivers of inflation are rising costs in services like healthcare, insurance, and air travel, with housing costs also continuing to put pressure on the economy. While some relief in housing costs is expected, they are likely to remain elevated compared to historical standards. The Federal Reserve forecasts that core inflation will reach 2.5% by 2025, with gradual declines to 2.2% in 2026 and 2.0% by 2027.
Trade Policies and Tariffs Add Complexity to Inflation Outlook
Economic policies from the incoming administration are further complicating the inflationary picture. Proposed actions such as higher tariffs, corporate tax reductions, and stricter immigration policies could add additional price pressures to the economy. Nobel Prize-winning economist Joseph Stiglitz has warned that widespread tariffs could spark a chain reaction, leading to rising costs, higher wage demands, and possible retaliatory tariffs from other countries.
“These policies have the potential to ignite an inflationary cycle,” Stiglitz cautioned, noting the risk of increased interest rates and a slowdown in global trade. BNP Paribas has forecasted that inflation could rise to 3.9% by late 2026, which might compel the Federal Reserve to pause or even reverse its interest rate cuts.
US Economy Demonstrates Resilience Amid Inflation Concerns
Despite concerns about inflation, the US economy has shown impressive resilience. Retail sales in November surpassed expectations, GDP growth remains solid, and unemployment remains low at around 4%. “The economy has several factors supporting its growth,” Luzzetti pointed out, noting the positive effects of the Federal Reserve’s interest rate cuts in 2024.
Nevertheless, economists caution that as long as inflation remains above 2.5%, the Federal Reserve may find it difficult to make further rate reductions in 2025. Even small increases in tariffs could contribute to higher costs and keep inflationary pressures intact.
Federal Reserve Faces Uncertainty in 2025
The Federal Reserve is preparing for a challenging year. Risks associated with inflation, potential policy changes, and global trade tensions have created significant uncertainty for investors. A recent Bank of America survey revealed growing concerns about a "no landing" scenario, where the economy continues to grow, but inflation remains stubbornly high.
“The US economy is showing remarkable resilience, but inflation continues to be the primary challenge,” Luzzetti stated. “The way policymakers respond to these inflationary pressures will determine whether the economy can continue to expand or if it will face obstacles in the year ahead.”
Also Read: Wall Street Braces for Fed’s Interest Rate Shift and 2025 Economic Challenges