US Regional Banks: S&P Global Downgrades Amidst Industry Challenges
Explore how S&P Global downgrades impact US regional banks amidst economic challenges, high interest rates, and profitability concerns. Gain insights into the evolving banking sector.

S&P Global's recent series of bond rating downgrades has illuminated the ongoing trials within the landscape of US regional banks. The banking sector continues to grapple with the complexities of high interest rates, elevated funding costs, and a shrinking profitability margin. Several banks, including Associated Bank, Comerica, Key Bank, UMB Financial Corp, and Valley National Bancorp, have faced rating downgrades that signify the enduring hurdles that the industry confronts. These events serve as a stark reminder of the turbulent waters that regional banks must navigate in the current economic climate.
Downgrades and Industry Landscape
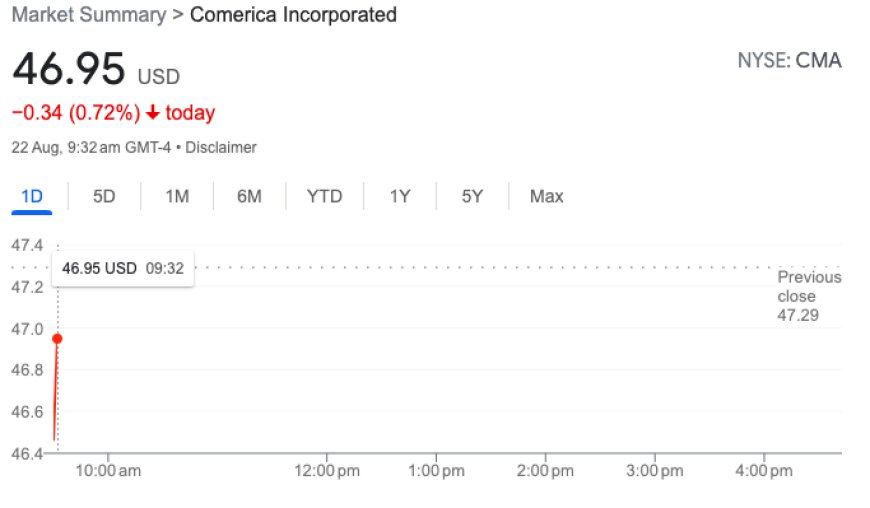
S&P Global took the unprecedented step of lowering bond ratings for several US regional banks, shedding light on the broader industry challenges. The downgrades for Associated Bank, Comerica, Key Bank, UMB Financial Corp, and Valley National Bancorp underscore the far-reaching impact of factors such as interest rate fluctuations and profitability pressures. These institutions, integral to local economies, are grappling with the complexities of maintaining financial stability amidst a dynamic economic environment.
Market Reaction and Industry Trends
The market response to S&P's downgrades has been palpable, with slight declines observed in premarket trading for the aforementioned banks. These movements are reflective of the broader concerns within the KBW Nasdaq regional bank index, which has experienced a 0.85% decrease in the current week. Amidst these shifts, regional banks are contending with the potential for the weakest monthly performance since the industry turmoil of March.
Systemic Vulnerabilities and Moody's Warning
The S&P Global downgrades follow a pattern established by Moody's Investors Service, which recently downgraded ten mid-sized institutions. Additionally, Moody's issued a warning regarding a review of six other lenders while assigning a negative outlook to eleven more. The potential for a broader industry downgrade from A+ to AA- is a looming concern, with far-reaching implications for major and smaller banks alike. This sentiment underscores the systemic vulnerabilities that regional banks must address in the face of ongoing economic fluctuations.
The Role of Interest Rates and Profitability
The driving force behind these challenges remains the Federal Reserve's determined effort to address inflation through elevated interest rates. The consequence of these measures has been a decline in the value of bonds held by banks and an increased need for banks to attract deposits with higher costs. This confluence of factors has led to reduced profitability and an elevated risk of liquidity challenges. In this evolving landscape, regional banks are struggling to strike a balance between profitability and financial stability.
Prospects and Resilience
While the outlook may appear challenging, S&P maintains a stable outlook for most US banks. This is attributed, in part, to the commendable resilience of the US economy and the implementation of an emergency bank funding program by regulators. Nevertheless, the anticipation is that profitability will likely witness further decline in the coming years as the Federal Reserve continues its quantitative tightening measures. This evolving landscape underscores the need for regional banks to adapt, innovate, and navigate these challenging waters with diligence and foresight.
Also Read: The Federal Reserve's Battle Against Inflation Continues with Rate Cut Considerations